Android 5.1.1
1. Android 網路連線機制並不允許同時有兩個device連外, Ethernet > wifi > mobile network. 會有一個評分機制在連線時決定哪個interface可以連線, 其他的連線則會被斷掉. 但是如果在user space使用command方式連線, 是可以看到一個以上的interface 拿到ip, 但是推測從android端連線出去時, 仍只會從priority高的device連出去.
frameworks/base/services/Java/com/android/server/ConnectivityService.java 將以下選項打開
private static final boolean DBG = true;
private static final boolean VDBG = true;
private static final boolean LOGD_RULES = true;
在log中就可以看到相關評分以及切換網路的動作, 可再往下追code.
參考以下網站將相關的code mark掉的話, 先連上wifi 再接上ethernet, 那wifi並不會強制斷線.但是若先接ethernet再接wifi, 那wifi也還是無法連上, 因為這邊只能將已連上的連線不斷線, 並不能搶走舊的連線.
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/37715525/use-multiple-network-interfaces-in-an-app
https://github.com/CyanogenMod/android_frameworks_base/blob/e49d5ea0858a765c22d8aa96cc660d4708a413fb/services/core/java/com/android/server/ConnectivityService.java#L4264
評分機制ethernet固定是150, wifi則根據RSSI來決定分數, 最高不超過100. 若兩者同分, 則以先連線的interface為主.
通過ConnectivityService之後, 如果是wifi連線, 接著會到WifiStatemachine
wifi state machine就會在各個state中切換, 來完成連線的各個動作, 這部份尚待研究.
接著往下會到JNI部份 frameworks/base/core/jni/android_net_wifi_Wifi.cpp
再往下就到wifi hardware部份 hardware/libhardware_legacy/wifi/wifi.c
在wifi.c時會根據傳入的參數來知道是要sta mode, ap mode or p2p mode. 根據知道是什麼mode之後會去reload相對應的fw.
以下是別人寫的ap mode啟動流程.
Setting->WifiManger->WifiService->WifiController->NetworkManagementService(wifiFirmwareReload)->NativeDaemonConnector(execute)->CommandListener->SoftapController(fwReloadSoftap)->wifi_get_fw_path
接著則會根據是什麼mode來決定要使用什麼tool以及讀取或create相關的conf檔案.
如果是sta mode的話, 就使用wpa_supplicant, ap mode則使用hostapd.
參考資料:
http://blog.csdn.net/kangear/article/details/14446527
http://blog.csdn.net/u010961631/article/details/48629601
http://blog.csdn.net/tankai19880619/article/details/42146287
http://blog.csdn.net/myarrow/article/details/8129607
http://blog.csdn.net/xusiwei1236/article/details/48495485
http://blog.sina.com.cn/s/blog_67e1c5cc0101ttqd.html
2017年7月24日 星期一
2017年7月18日 星期二
Uboot passes arguments to kernel
u-boot 要傳參數到kernel可使用 setenv bootargs
cmd line sample
# setenv bootargs androidboot.selinux=disable
# saveenv
code sample
setenv("bootargs", "androidboot.selinux=disable");
但是在android時, 會在image-android.c中的android_image_get_kernel讀取boot.img中的bootargs
boot.img的bootargs放在 BOARD_KERNEL_CMDLINE
BOARD_KERNEL_CMDLINE := console=ttymxc4,115200 init=/init
需注意的是如果code當中有設bootargs的話, 那在android_image_get_kernel就不會使用BOARD_KERNEL_CMDLINE設定的bootargs
接著bootargs會傳到proc/cmdline, 可使用cat來確認傳入的parameter.
若要再交給android做為properties使用, 那可以在bootargs增加androidboot.xxx=xxx
在system/core/init/init.c當中會去處理bootargs.
在import_kernel_nv當中會將androidboot.xxx都換成ro.boot.xxx
所以如果一開始有設置androidboot.selinux=disable的話, 在經過這邊之後會被換成ro.boot.selinux=disable, boot進android之後使用getprop就可以看到了.
另外一些特定的properties則會經過export_kernel_boot_props再parsing一次.
cmd line sample
# setenv bootargs androidboot.selinux=disable
# saveenv
code sample
setenv("bootargs", "androidboot.selinux=disable");
但是在android時, 會在image-android.c中的android_image_get_kernel讀取boot.img中的bootargs
boot.img的bootargs放在 BOARD_KERNEL_CMDLINE
BOARD_KERNEL_CMDLINE := console=ttymxc4,115200 init=/init
需注意的是如果code當中有設bootargs的話, 那在android_image_get_kernel就不會使用BOARD_KERNEL_CMDLINE設定的bootargs
int len = 0;
if (*hdr->cmdline) {
len += strlen(hdr->cmdline);
}
char *bootargs = getenv("bootargs");
if (bootargs)
len += strlen(bootargs);
char *newbootargs = malloc(len + 2);
if (!newbootargs) {
puts("Error: malloc in android_image_get_kernel failed!\n");
return -ENOMEM;
}
*newbootargs = '\0';
if (bootargs) {
strcpy(newbootargs, bootargs);
} else if (*hdr->cmdline) {
strcat(newbootargs, hdr->cmdline);
}
接著bootargs會傳到proc/cmdline, 可使用cat來確認傳入的parameter.
若要再交給android做為properties使用, 那可以在bootargs增加androidboot.xxx=xxx
在system/core/init/init.c當中會去處理bootargs.
static void process_kernel_cmdline(void)
{
/* don't expose the raw commandline to nonpriv processes */
chmod("/proc/cmdline", 0440);
/* first pass does the common stuff, and finds if we are in qemu.
* second pass is only necessary for qemu to export all kernel params
* as props.
*/
import_kernel_cmdline(0, import_kernel_nv); //read kernel parameter here
if (qemu[0])
import_kernel_cmdline(1, import_kernel_nv);
/* now propogate the info given on command line to internal variables
* used by init as well as the current required properties
*/
export_kernel_boot_props();
}
void import_kernel_cmdline(int in_qemu,
void (*import_kernel_nv)(char *name, int in_qemu))
{
char cmdline[2048];
char *ptr;
int fd;
fd = open("/proc/cmdline", O_RDONLY);
if (fd >= 0) {
int n = read(fd, cmdline, sizeof(cmdline) - 1);
if (n < 0) n = 0;
/* get rid of trailing newline, it happens */
if (n > 0 && cmdline[n-1] == '\n') n--;
cmdline[n] = 0;
close(fd);
} else {
cmdline[0] = 0;
}
ptr = cmdline;
while (ptr && *ptr) {
char *x = strchr(ptr, ' ');
if (x != 0) *x++ = 0;
import_kernel_nv(ptr, in_qemu);
ptr = x;
}
}
在import_kernel_nv當中會將androidboot.xxx都換成ro.boot.xxx
static void import_kernel_nv(char *name, int for_emulator)
{
char *value = strchr(name, '=');
int name_len = strlen(name);
if (value == 0) return;
*value++ = 0;
if (name_len == 0) return;
if (for_emulator) {
/* in the emulator, export any kernel option with the
* ro.kernel. prefix */
char buff[PROP_NAME_MAX];
int len = snprintf( buff, sizeof(buff), "ro.kernel.%s", name );
if (len < (int)sizeof(buff))
property_set( buff, value );
return;
}
if (!strcmp(name,"qemu")) {
strlcpy(qemu, value, sizeof(qemu));
} else if (!strncmp(name, "androidboot.", 12) && name_len > 12) {
const char *boot_prop_name = name + 12;
char prop[PROP_NAME_MAX];
int cnt;
cnt = snprintf(prop, sizeof(prop), "ro.boot.%s", boot_prop_name); //change to ro.boot.xxx here
if (cnt < PROP_NAME_MAX)
property_set(prop, value);
}
}
所以如果一開始有設置androidboot.selinux=disable的話, 在經過這邊之後會被換成ro.boot.selinux=disable, boot進android之後使用getprop就可以看到了.
另外一些特定的properties則會經過export_kernel_boot_props再parsing一次.
struct {
const char *src_prop;
const char *dest_prop;
const char *def_val;
} prop_map[] = {
{ "ro.boot.serialno", "ro.serialno", "", },
{ "ro.boot.mode", "ro.bootmode", "unknown", },
{ "ro.boot.baseband", "ro.baseband", "unknown", },
{ "ro.boot.bootloader", "ro.bootloader", "unknown", },
};
2017年6月21日 星期三
Jenkins tips
Jenkins 注意的點, for Android Repo project
1. Use Gerrit Repo plugin, Manifest Branch的部份不需填入branch name. 在後面shell command部份使用repo start切branch即可, manifest branch亂填會導致xml檔錯誤.
2. Gerrit Repo plugin不是非常好用, 有些command的參數無法自己下, 推薦還是使用shell command直接做想下的repo command即可.
3. Gerrit trigger plugin: 先參考plug in wiki上在Gerrit server上做好Jenkins帳號的權限設定.
https://wiki.jenkins-ci.org/display/JENKINS/Gerrit+Trigger#GerritTrigger-SetUp
4. Gerrit trigger plugin: Gerrit server如果設好之後test connection就會顯示success, 如果test ok但是上層的gerrit server status一直有問題的話, 重開Jenkins server. 如果ssh key有改名或換檔案, 也需要重開Jenkins server.
5. Gerrit trigger plugin: 在工作中的設定, path 設**會去monitor 目錄下所有的project, Branches設plain branch_name.
6. Gerrit trigger plugin: plugin可使用下面這行command, 就會merge進此patch,
repo download $GERRIT_PROJECT $GERRIT_CHANGE_NUMBER/$GERRIT_PATCHSET_NUMBER
Note: merge之後並不會自動revert, code會留在目錄中. 需注意$GERRIT_PROJECT, 他會去抓gerrit上的project name, 如果project path有多幾層的話, 可以用sed刪除字串再丟回download path.
7. Shell command中如果使用cp, rm, mkdir需注意權限. copy檔案到/var/lib/jenkins/以外的路徑需先把目錄權限設到777
1. Use Gerrit Repo plugin, Manifest Branch的部份不需填入branch name. 在後面shell command部份使用repo start切branch即可, manifest branch亂填會導致xml檔錯誤.
2. Gerrit Repo plugin不是非常好用, 有些command的參數無法自己下, 推薦還是使用shell command直接做想下的repo command即可.
3. Gerrit trigger plugin: 先參考plug in wiki上在Gerrit server上做好Jenkins帳號的權限設定.
https://wiki.jenkins-ci.org/display/JENKINS/Gerrit+Trigger#GerritTrigger-SetUp
4. Gerrit trigger plugin: Gerrit server如果設好之後test connection就會顯示success, 如果test ok但是上層的gerrit server status一直有問題的話, 重開Jenkins server. 如果ssh key有改名或換檔案, 也需要重開Jenkins server.
5. Gerrit trigger plugin: 在工作中的設定, path 設**會去monitor 目錄下所有的project, Branches設plain branch_name.
6. Gerrit trigger plugin: plugin可使用下面這行command, 就會merge進此patch,
repo download $GERRIT_PROJECT $GERRIT_CHANGE_NUMBER/$GERRIT_PATCHSET_NUMBER
Note: merge之後並不會自動revert, code會留在目錄中. 需注意$GERRIT_PROJECT, 他會去抓gerrit上的project name, 如果project path有多幾層的話, 可以用sed刪除字串再丟回download path.
7. Shell command中如果使用cp, rm, mkdir需注意權限. copy檔案到/var/lib/jenkins/以外的路徑需先把目錄權限設到777
2017年3月22日 星期三
使用Eclipse開發Linux Kernel 設定
來源: http://maxron.blogspot.tw/2012/05/eclipselinux-kernel.html?view=flipcard
下面文章說3.5.1 + CDT ,不過,基本上只要下載 eclipse forr c/c++ 的版本就有附帶CDT了。功能上就和 source insight 是一樣的,是可以取代source insight 的一種選擇
下面文章說3.5.1 + CDT ,不過,基本上只要下載 eclipse forr c/c++ 的版本就有附帶CDT了。功能上就和 source insight 是一樣的,是可以取代source insight 的一種選擇
Here are some steps that I've found to get the CDT to work well with the Linux kernel source. If you exclude some of these steps, it may still work to a large degree, but some things may not work exactly right; for example it may find the wrong include file for a C file.
Anyway, as you do these steps, I think you may understand how they assist the indexer to do a good job for the Linux kernel source.
Disclaimer: these steps were developed for Eclipse 3.5.1 + CDT 6.0.0.
- Download and install Eclipse plus the CDT.
- Configure and build your kernel to define CONFIG_* and generate autoconf.h. This can be done before or after downloading and installing Eclipse.
- Ensure that you have the right kernel source (e.g. make sure you are on the right git branch). If you check out another branch later, that's ok, but you will need to re-index the source, and that takes about 20 minutes.
- Start up Eclipse.
- Click File->New->C Project
- Fill in a project name like my_kernel
- Uncheck the Use default location box and type in the root directory of your kernel into the Location box.
- In the Project type: pane, click the Makefile project and select Empty Project
- On the right side, select Linux GCC
- Click Advanced settings... and a Properties dialog will pop up.
- Select Resource on the left, and then in the Text file encoding section, select Other and ISO-8859-1 in the box, then click Apply
- Select C/C++ Build on the left.
- Click on Discovery Options
- At the bottom of the screen where it says Compiler invocation arguments, insert "-include include/generated/autoconf.h" at the beginning of that line. Also insert any other compiler options you may need that are not the default, such as "-m64" (Note: for older kernels [pre-2.6.36?], the location of autoconf.h is include/linux/autoconf.h) <-- cannot find this
- You may also need to change the compiler command from gcc to whatever compiler you are using (e.g. you are using a cross compiler).
- Open the C/C++ General selection on the left.
- Click on Indexer
- Checkmark the Enable project specific setttings box.
- Uncheck Index source files not included in the build
- Clear out the Files to index up-front box.
- Click on Paths and Symbols on the left.
- Select the Includes tab and then select GNU C
- Click Add...
- Click Workspace... then select your kernel's include directory
- Do another Add, Workspace and add arch/architecture/include, e.g., arch/powerpc/include
- Click the # Symbols tab
- Click Add...
- Set the name to __KERNEL__
- Set the value to 1 and click OK
- Click the Source Location tab
- Click the twisty for your project.
- Select the Filter item and click Edit Filter...
- Click Add Multiple... and then select all of the arch/* directories in your kernel source that will not be used (i.e. all the ones that are not for the architecture you are using)
- Click OK and OK again to dismiss that dialog.
- Click OK on the Properties dialog.
- Click Finish on the C Project dialog.
- Right click on the project and select Index then select Rebuild
- It will take about 20 minutes or so to complete.
Notes:
- Adding include and arch/architecture/include only gets you a couple of the common include paths. To fully index all of the kernel, you would have to add dozens of paths, unfortunately. Header (.h) files are not present only in include directories. For this reason, I advise against using PTP's remote indexing capability for the linux kernel, because what happens is that it will report thousands of errors in locating header files, and the process of reporting those errors over a possibly long-latency link, will cause the indexing to take many hours.
- If you change any of your CONFIG_* settings, in order for Eclipse to recognize those changes, you must do a "build" from within Eclipse. Note, this does not mean to re-build the index; this means to build the kernel, by having Eclipse invoke make (this is normally bound to the Ctrl-B key in Eclipse). Only after a build operation, will Eclipse regenerate the compilation #defines it uses when analyzing the source during indexing and editing.
- The background color of "Quick Context View" will be dark if the Ambiance theme in Ubuntu is selected.
2016年8月11日 星期四
Git常用狀況
git的四個folder
remote repository<---->local repository<---->stage<---->working directory
1. 初始download 資料夾from server
$git clone server_name aa aa是folder name可以自己建
2. 修改完code之後要傳上server
$git add filenameA filenameB 將檔案都丟進stage
$git commit -m "log message" 將檔案commit上local repository
$git push 將修改的部分真正傳到server
git add的部分,如果有把握的話可以使用$git add . 會將整個working directory有修改過的檔案都丟進stage,如果沒把握請勿使用,避免傳上不知道狀況的檔案.
3. 更新自己的code到server上最新的code
$git fetch 更新local repository與remote repository一致
$git merge origin/master 將working directory更新與server上一致,如果有conflict會出現在這邊
如果要看server上改了什麼在git fetch完之後
$git checkout origin/master
$gitk -a
4. 修改conflict的方式
$ vim conflict_file_name
進去之後會看到類似的情況
<<<<<<< c97e4c60de36e44afd801cf0d22aab1399e9269c
123
=======
456
>>>>>>> conflict example
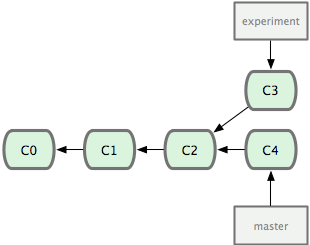
remote repository<---->local repository<---->stage<---->working directory
1. 初始download 資料夾from server
$git clone server_name aa aa是folder name可以自己建
2. 修改完code之後要傳上server
$git add filenameA filenameB 將檔案都丟進stage
$git commit -m "log message" 將檔案commit上local repository
$git push 將修改的部分真正傳到server
git add的部分,如果有把握的話可以使用$git add . 會將整個working directory有修改過的檔案都丟進stage,如果沒把握請勿使用,避免傳上不知道狀況的檔案.
3. 更新自己的code到server上最新的code
$git fetch 更新local repository與remote repository一致
$git merge origin/master 將working directory更新與server上一致,如果有conflict會出現在這邊
如果要看server上改了什麼在git fetch完之後
$git checkout origin/master
$gitk -a
4. 修改conflict的方式
$ vim conflict_file_name
進去之後會看到類似的情況
<<<<<<< c97e4c60de36e44afd801cf0d22aab1399e9269c
123
=======
456
>>>>>>> conflict example
<<<跟>>>中間的部分是git無法merge的部分,===上面是A版的code,===下面是B版的code,自己修改完之後,記得將<<< >>> ===都刪除, press esc-->:-->wq 儲存離開
5. rollback code的方法
如果是本機上的單支code改亂了,要revert到沒改過的狀況
$git checkout file_name
如果是整個資料夾都改壞了,要全部檔案rollback
$git reset --hard HEAD
6. rollback小板的方法
如果只是某幾支檔案要退回xx版,來驗證東西的話
$git checkout xxx_version fileA fileB fileC 可以將特定檔案rollback回xxx version
2016年8月9日 星期二
Git 基本指令
1. git config --list list all config
2. git config --global xxxxx ex, git config --global user.name "Jerry" change user name
3. git init 在任何想要initial成git folder的地方下
4. git clone http://127.0.0.1/ xxxx clone遠端server的folder下來, xxxx是抓下來的folder名字
5. git status 確認目前有任何的檔案的被更動
6. git add filename 將修改過的檔案加入stage(index)
a. git add . 將所有修改過的檔案加入
b. git add -i 使用互動式介面來修改檔案
7. git commit 將在stage中的檔案commit進去
a. git commit -m "xxxxx" 直接加入commit message
8. git log 查看過去commit的log
a. git log --stat detail information
b. git log xxxx 顯示出特定版本的log
c. git log filename 特定檔案的log
d. git log -p filename 特定檔案詳細更改的log
ex:
commit 7e56e3f83c0ac52218b25db1514423d07ae0449d
Author: Jerry Lain <hyde545@gmail.com>
Date: Wed Aug 3 17:32:06 2016 +0800
14. git reset 回復到某一版本
a. git reset --hard HEAD 將所有的檔案都回復到HEAD版本
b. git reset HEAD 本地資料夾中的資料不改,stage的檔案回復,線拉回前一版
c. git reset --soft HEAD 只有線拉回前一版
d. git reset HEAD^^ , 也能使用git reset HEAD~2, 回到兩版之前的資料
b and c的情況因為線已經拉回前一版了,所以本地中的檔案不會有任何變動,但是git status會變成需add and commit
退版的方法
1. git checkout xxversion file_a file_b file_c 只有本機檔案會更動.
2. git revert xxversion 會將xx version更改的檔案rollback並commit進history
3. git rebase -i xxxversion 會列出中間所有version,刪掉那行就會rollback,也會從history中刪除,不留痕跡.
12. git push 將目前的folder push回原本clone的位置
remote repository, origin/xxx branch
$git checkout origin/master 切回遠端的master
git pull = git fetch + git merge origin/master
git fetch先將local的repository的origin/master更新到server上的位置,再將local master與origin/master merge整個動作就等於 git pull, 所以建議將兩個動作分開, 多使用git fetch
git fetch之後如果要看remote master改了什麼,需要先checkout to origin/master再下gitk才能看
push new branch
git push origin aabranch aabranch必須是本機上有的branch 而不能直接建新branch到remote
刪除branch
git branch -d aabranch 本機刪除
git push origin :aabranch remote刪除
2. git config --global xxxxx ex, git config --global user.name "Jerry" change user name
3. git init 在任何想要initial成git folder的地方下
4. git clone http://127.0.0.1/ xxxx clone遠端server的folder下來, xxxx是抓下來的folder名字
5. git status 確認目前有任何的檔案的被更動
6. git add filename 將修改過的檔案加入stage(index)
a. git add . 將所有修改過的檔案加入
b. git add -i 使用互動式介面來修改檔案
7. git commit 將在stage中的檔案commit進去
a. git commit -m "xxxxx" 直接加入commit message
8. git log 查看過去commit的log
a. git log --stat detail information
b. git log xxxx 顯示出特定版本的log
c. git log filename 特定檔案的log
d. git log -p filename 特定檔案詳細更改的log
ex:
commit 7e56e3f83c0ac52218b25db1514423d07ae0449d
Author: Jerry Lain <hyde545@gmail.com>
Date: Wed Aug 3 17:32:06 2016 +0800
$git log 7e56 7e56e3f8 7e56e3f83c0a 都可以
9. git branch list出現在有哪些branch並告訴你現在在哪個branch
a. git branch xxx 開出一隻新的branch
b. git branch -d xxx 移除xxx branch
10. gitk --all GUI介面list出來所有的commit log
11. git checkout xxx 切換到xxx branch
a. git checkout fiename 將單支檔案回復到未改過的狀態,如同SVN的revert
b. git checkout xxxversion filename 切換本機特定檔案跟stage index到某一版本
a. git checkout fiename 將單支檔案回復到未改過的狀態,如同SVN的revert
b. git checkout xxxversion filename 切換本機特定檔案跟stage index到某一版本
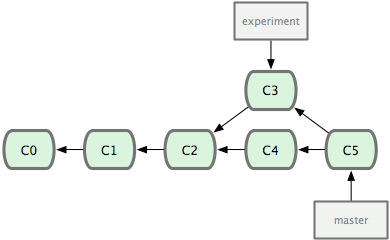
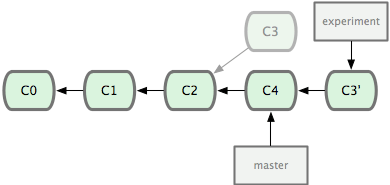
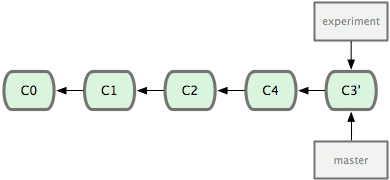
12. git rebase yyy 將目前branch的修改base on yyy branch的功能合併起來,rebase是在yyy branch中更改一份跟原本branch一樣的修改. 在branch出來的位置rebase回master. 否則會變成在branch中更改master,不太符合master是主要分支的概念. rebase完之後需再回到master做一次merge. 這樣的情況下最後得到的結果會與merge一樣,只是在git線圖上可以得到一個更簡潔的圖. rebase之後所有修改的部分都在同一支線中,如果要reset回去的話就不會有分支的問題,直接merge的話,reset回去到分支的版本中會有branch A與branch B兩隻分支檔案不同的問題.
由於rebase是在master上再修改一次,所以branch 的每個checksum會改變.
由於rebase是在master上一版一版修改的加上去,所以conflict的部分也是需要一版一版解決.
merge則是將master與branch合併之後產生一版新的版本,所以conflict一次解決就好.
不要rebase在遠端的資料庫,只能在push之前將local資料庫的history整理好,因為rebase會更改SHA-1的值,rebase遠端的資料庫會將遠端的history打亂,造成其他使用者重複合併修改過的內容以致history大亂. 可以參考https://git-scm.com/book/zh-tw/v1/Git-%E5%88%86%E6%94%AF-%E5%88%86%E6%94%AF%E7%9A%84%E8%A1%8D%E5%90%88 最下方衍合的風險
git rebase onto new-version current-version 將current version"嫁接"到new version上
https://blog.yorkxin.org/2011/07/29/git-rebase
13. git merge xxx merge是將現在的分支跟xxx分支合併後產生一版新的提交. 在master merge xxx branch才會讓master分支繼續往下走.
遇到conflict時,修改完之後都需要先git add . 將修改的檔案加入stage,接著
rebase: git rebase --continue 讓他繼續做rebase的動作.
merge: git commit 讓他commit一版
由於rebase是在master上再修改一次,所以branch 的每個checksum會改變.
由於rebase是在master上一版一版修改的加上去,所以conflict的部分也是需要一版一版解決.
merge則是將master與branch合併之後產生一版新的版本,所以conflict一次解決就好.
不要rebase在遠端的資料庫,只能在push之前將local資料庫的history整理好,因為rebase會更改SHA-1的值,rebase遠端的資料庫會將遠端的history打亂,造成其他使用者重複合併修改過的內容以致history大亂. 可以參考https://git-scm.com/book/zh-tw/v1/Git-%E5%88%86%E6%94%AF-%E5%88%86%E6%94%AF%E7%9A%84%E8%A1%8D%E5%90%88 最下方衍合的風險
git rebase onto new-version current-version 將current version"嫁接"到new version上
https://blog.yorkxin.org/2011/07/29/git-rebase
13. git merge xxx merge是將現在的分支跟xxx分支合併後產生一版新的提交. 在master merge xxx branch才會讓master分支繼續往下走.
遇到conflict時,修改完之後都需要先git add . 將修改的檔案加入stage,接著
rebase: git rebase --continue 讓他繼續做rebase的動作.
merge: git commit 讓他commit一版
14. git reset 回復到某一版本
a. git reset --hard HEAD 將所有的檔案都回復到HEAD版本
b. git reset HEAD 本地資料夾中的資料不改,stage的檔案回復,線拉回前一版
c. git reset --soft HEAD 只有線拉回前一版
d. git reset HEAD^^ , 也能使用git reset HEAD~2, 回到兩版之前的資料
b and c的情況因為線已經拉回前一版了,所以本地中的檔案不會有任何變動,但是git status會變成需add and commit
退版的方法
1. git checkout xxversion file_a file_b file_c 只有本機檔案會更動.
2. git revert xxversion 會將xx version更改的檔案rollback並commit進history
3. git rebase -i xxxversion 會列出中間所有version,刪掉那行就會rollback,也會從history中刪除,不留痕跡.
12. git push 將目前的folder push回原本clone的位置
沒有merge到master的資料無法push回去
master branch 是主要的branch,所有修改完的東西都再回到master branch
remote repository, origin/xxx branch
$git checkout origin/master 切回遠端的master
git pull = git fetch + git merge origin/master
git fetch先將local的repository的origin/master更新到server上的位置,再將local master與origin/master merge整個動作就等於 git pull, 所以建議將兩個動作分開, 多使用git fetch
git fetch之後如果要看remote master改了什麼,需要先checkout to origin/master再下gitk才能看
push new branch
git push origin aabranch aabranch必須是本機上有的branch 而不能直接建新branch到remote
刪除branch
git branch -d aabranch 本機刪除
git push origin :aabranch remote刪除
git - 後面接一個字的縮寫ex. git config -l
git -- 後面接全名 ex. git config --list
push-pull, open-drain
Push-pull:
Open-Drain:
open drain, 外部需有pull up電阻, 內部floating
push pull外部則不須pull up, 由內部control
Push-pull輸出,實際上內部是用了兩個電晶體(transistor),此處分別稱為top transistor和bottom transistor。通過開關對應的電晶體,輸出對應的電平。top transistor打開(bottom transistor關閉),輸出為高電平;bottom transistor打開(top transistor關閉),輸出低電平。Push-pull即能夠漏電流(sink current),又可以集電流(source current)。其也許有,也許沒有另外一個狀態:高阻抗(high impedance)狀態。除非Push-pull需要支援額外的高阻抗狀態,否則不需要額外的上拉電阻。
Open-Drain:
Open-drain輸出,則是比push-pull少了個top transistor,只有那個bottom transistor。(就像push-pull中的那樣)當bottom transistor關閉,則輸出為高電平。此處沒法輸出高電平,想要輸出高電平,必須外部再接一個上拉電阻(pull-up resistor)。Open-drain只能夠漏電流(sink current),如果想要集電流(source current),則需要加一個上拉電阻。
常見的GPIO的模式可以配置為open-drain或push-pull,具體實現上,常為通過配置對應的寄存器的某些位元來配置為open-drain或是push-pull。當我們通過CPU去設置那些GPIO的配置寄存器的某位元(bit)的時候,其GPIO硬體IC內部的實現是,會去打開或關閉對應的top transistor。相應地,如果設置為了open-d模式的話,是需要上拉電阻才能實現,也能夠輸出高電平的。因此,如果硬體內部(internal)本身包含了對應的上拉電阻的話,此時會去關閉或打開對應的上拉電阻。如果GPIO硬體IC內部沒有對應的上拉電阻的話,那麼你的硬體電路中,必須自己提供對應的外部(external)的上拉電阻。而push-pull輸出的優勢是速度快,因為線路(line)是以兩種方式驅動的。而帶了上拉電阻的線路,即使以最快的速度去提升電壓,最快也要一個常量的R×C的時間。其中R是電阻,C是寄生電容(parasitic
capacitance),包括了pin腳的電容和板子的電容。但是,push-pull相對的缺點是往往需要消耗更多的電流,即功耗相對大。而open-drain所消耗的電流相對較小,由電阻R所限制,而R不能太小,因為當輸出為低電平的時候,需要sink更低的transistor,這意味著更高的功耗。(此段原文:because the lower
transistor has to sink that current when the output is low; that means higher
power consumption.)而open-drain的好處之一是,允許你cshort(?)多個open-drain的電路,公用一個上拉電阻,此種做法稱為wired-OR連接,此時可以通過拉低任何一個IO的pin腳使得輸出為低電平。為了輸出高電平,則所有的都輸出高電平。此種邏輯,就是“線與”的功能,可以不需要額外的gate電路來實現此部分邏輯。
對於GPIO的模式的設置,在不考慮是否需要額外的上拉電阻的情況下,是設置為open-drain還是push-pull,說到底,還是個權衡的問題:
如果你想要電平轉換速度快的話,那麼就選push-pull,但是缺點是功耗相對會大些。
如果你想要功耗低,且同時具有“線與”的功能,那麼就用open-drain的模式。(同時注意GPIO硬體模組內部是否有上拉電阻,如果沒有,需要硬體電路上添加額外的上拉電阻)
open drain, 外部需有pull up電阻, 內部floating
push pull外部則不須pull up, 由內部control
訂閱:
文章 (Atom)